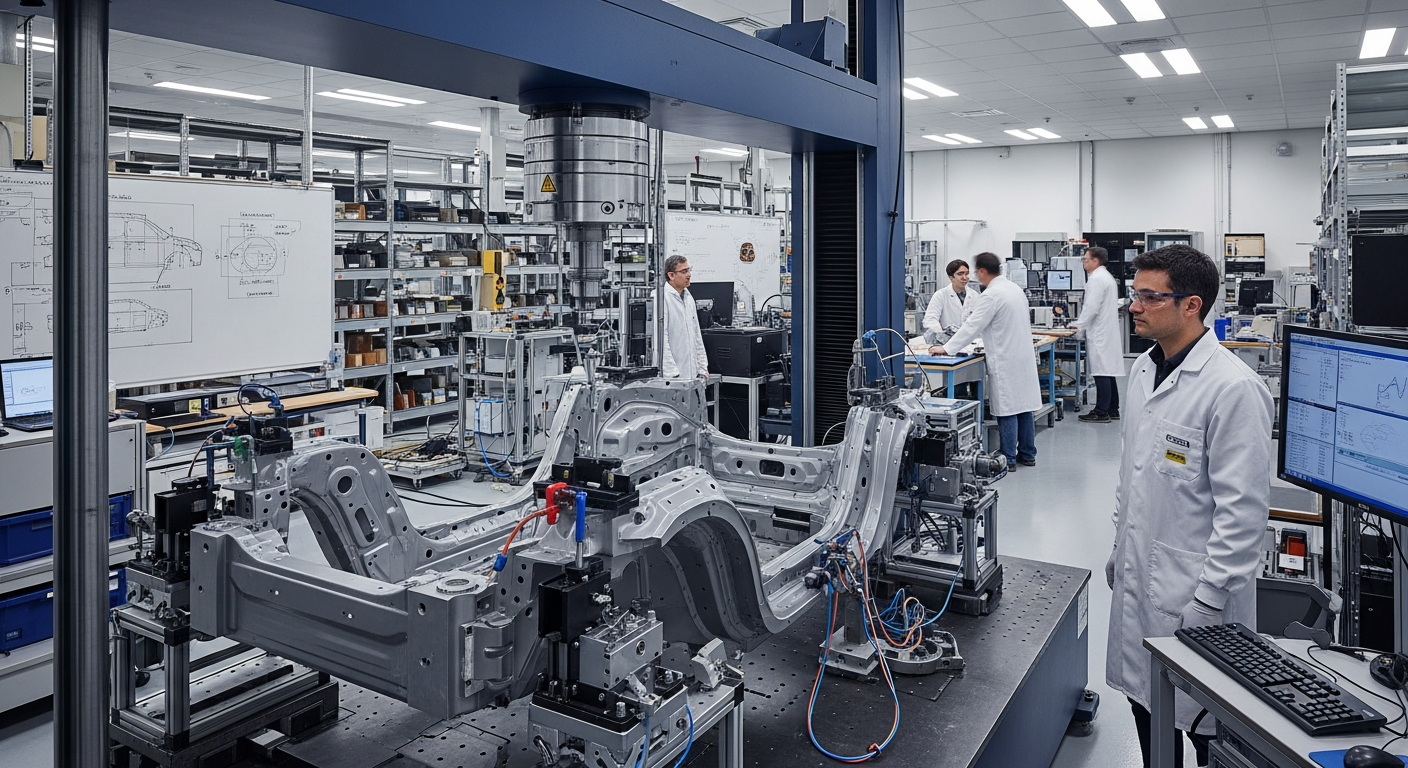
The Impact of Digitalization on Automotive Design
Digitalization has profoundly transformed various industries, and the automotive sector is no exception. From initial concept sketches to final production, digital technologies have reshaped how vehicles are conceived, developed, and manufactured. This shift has not only streamlined processes but also opened new avenues for innovation, influencing everything from aesthetic appeal to functional performance and the overall user experience in modern transport. Understanding this evolution is crucial to appreciating the current state and future trajectory of automotive design worldwide.
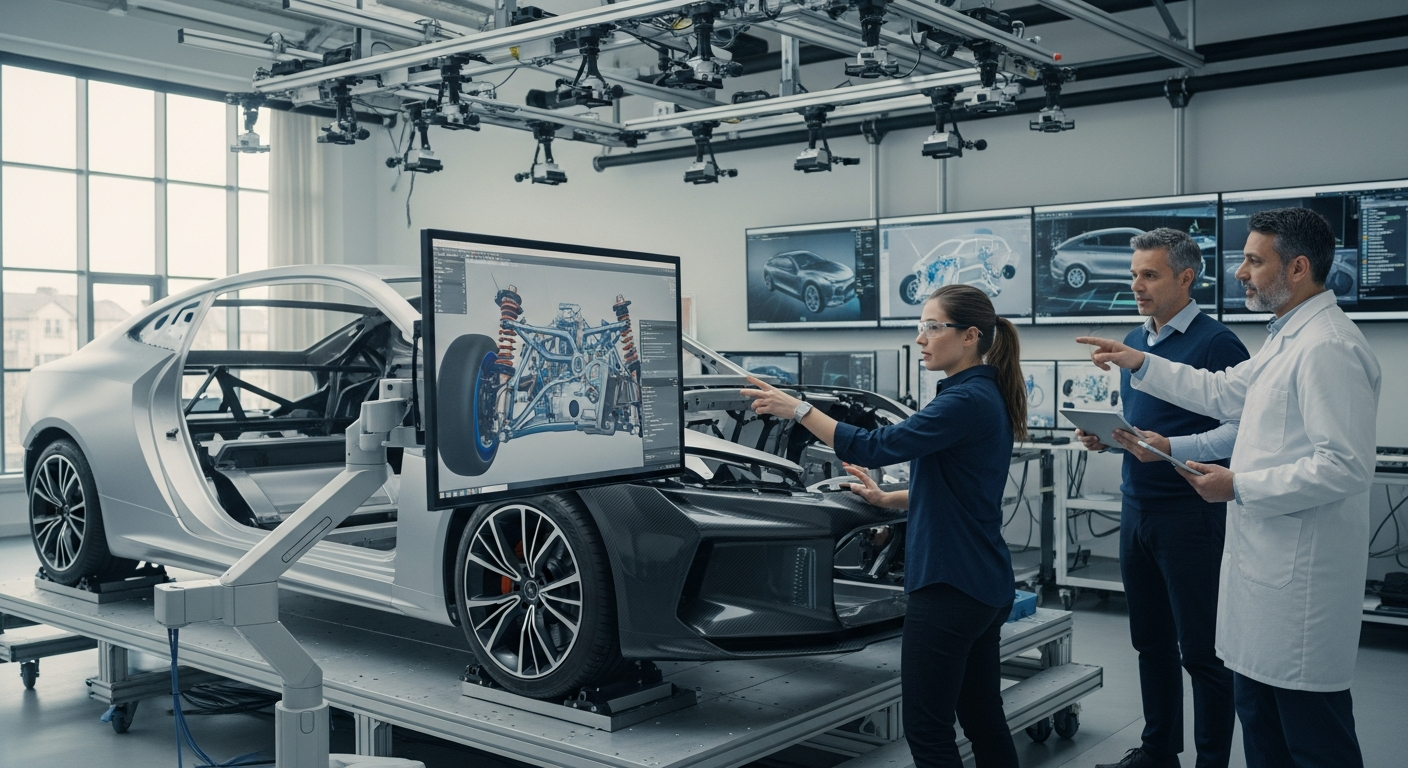
Digital Tools Shaping Vehicle Design
The integration of advanced digital tools has revolutionized the initial phases of automotive design. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software allows designers to create intricate 3D models with precision, enabling rapid iteration and visualization of various design concepts. This technology facilitates a more collaborative environment where teams can work on a single vehicle model simultaneously, accelerating the design cycle. Furthermore, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are increasingly used to immerse designers and engineers in virtual prototypes, allowing them to experience and evaluate designs in a realistic context before physical models are even built. This significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods, fostering greater innovation in the overall aesthetic and ergonomic design of the vehicle.
Enhancing Automotive Safety and Performance
Digitalization plays a critical role in advancing both the safety and performance aspects of modern automotive engineering. Simulation software allows engineers to virtually test vehicle components and entire systems under various conditions, predicting how a vehicle will behave in a collision or how its aerodynamics will impact fuel efficiency. This includes advanced crash simulations that help optimize structural designs for occupant protection, enhancing overall safety. Digital twins, virtual replicas of physical vehicles, enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, contributing to the longevity and consistent performance of the engine and other critical systems. These technologies allow for fine-tuning of suspension, steering, and braking systems, leading to superior driving dynamics and a more responsive feel on the road.
The Role of Digitalization in Electric and Hybrid Mobility
The transition towards electric and hybrid vehicles is heavily reliant on digital innovation. Digitalization aids in the complex design of battery packs, electric motors, and power electronics, optimizing their integration within the vehicle’s architecture. Software development is central to managing the intricate energy flow, charging systems, and regenerative braking in these advanced powertrains. The ability to simulate battery performance and degradation over time allows for more efficient design and better range prediction. This emphasis on digital systems supports the ongoing evolution of sustainable transport solutions, addressing concerns about fuel consumption and environmental impact, and paving the way for more efficient and appealing electric and hybrid vehicle designs.
Innovative Materials and Manufacturing Technology
Digitalization extends beyond design to influence the materials used and the manufacturing processes in the automotive industry. Advanced simulation tools help identify and test new lightweight materials, such as composites and high-strength alloys, which are crucial for improving vehicle performance and fuel economy. Digital manufacturing technologies, including 3D printing and robotic automation, allow for the production of complex parts with greater precision and efficiency. This enables designers to experiment with forms and structures that were previously impossible or too costly to produce, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in terms of both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. The integration of these technologies results in more robust, lighter, and more sustainably produced vehicles.
Future Trends in Transport Design Systems
The future of automotive design will continue to be shaped by ongoing digitalization, particularly in the realm of autonomous driving and connected car systems. Digital platforms are foundational for developing and testing the complex algorithms that govern self-driving vehicles, including sensor integration and decision-making processes. The growing connectivity of vehicles, allowing them to communicate with each other and with infrastructure, necessitates sophisticated digital architecture. This will influence interior design, shifting focus from traditional driving controls to passenger comfort and in-car entertainment, transforming the travel experience. The continuous innovation in digital technology promises a future where mobility is safer, more efficient, and seamlessly integrated into daily life, redefining the very concept of driving and road usage.
Conclusion
Digitalization has fundamentally reshaped every aspect of automotive design, from the initial conceptualization of a vehicle to its manufacturing and its subsequent performance on the road. It has empowered designers and engineers to push boundaries, innovate rapidly, and create vehicles that are safer, more efficient, and better integrated with emerging technologies. The ongoing advancements in digital tools and methodologies will continue to drive the evolution of the automotive sector, promising a future of transport that is both technologically sophisticated and environmentally conscious, impacting mobility and the driving experience for consumers worldwide.





